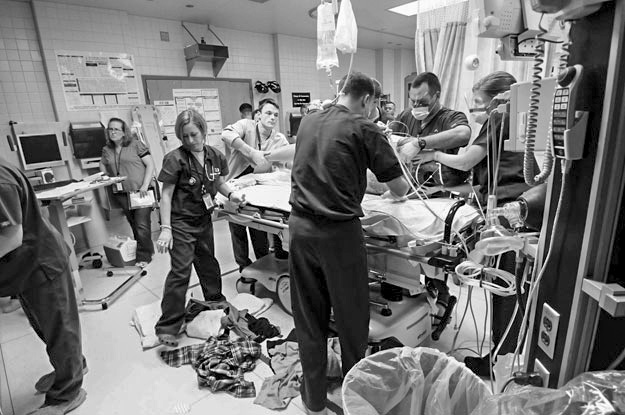
Acute medical situations, such as life-threatening illnesses and injuries, are the primary focus of emergency care. Doctors specializing in emergency medicine are prepared to treat patients in a medical emergency, such as an injury or severe illness. Below is a summary of the coursework and clinical experience you’ll need to become an emergency medicine specialist.
Emergency medicine subspecialists like Dr Michael Hilton are required to have specific training and education. A lot of schooling and experience are needed to become an expert in emergency medicine. To begin, get a bachelor’s degree from a recognized institution. Studying biology, chemistry, physics, and mathematics is recommended for anyone considering a career in medicine. However, they are not required. Volunteering or working in a healthcare setting is also highly encouraged.
School Of Medicine And Residency
After earning a bachelor’s degree, the next logical step is to enroll in medical school. Students spend four years learning the ins and outs of the human body and its systems, including anatomy, physiology, and pharmacology. Students in their third and fourth years of medical school participate in clinical rotations in various medical specialties, including emergency medicine, to get practical experience in the field.
To practice emergency medicine after graduating from medical school, residents must finish an emergency medicine residency program. The duration of a residency program ranges from three to four years, and throughout that time, residents learn to recognize and manage medical emergencies. Intubation, chest tube insertion, and central line installation are among the operations that trainees will get practice with during their residency.
Board Approval
Suppose an individual wants to become an emergency medicine specialist like Dr Michael Hilton. In that case, they are required to finish a residency program and take a board exam given by the American Board of Emergency Medicine (ABEM). First, a candidate for board certification in emergency medicine must demonstrate that they have a firm grasp of the written and oral tests.
Grants And Scholarships
Some emergency medical professionals are offered fellowships in subspecialties of emergency medicine, such as critical care medicine, pediatric emergency medicine, and emergency ultrasonography, to expand their knowledge in these areas. Fellowships and additional training in specialized areas of emergency care often run between one and two years.
Training And Development For Working Professionals
To do their jobs effectively, emergency medicine professionals must be abreast of the latest developments in their field. In order to keep up with the rapid pace of change in emergency medicine, professionals in the field can participate in various continuing education opportunities, including courses, conferences, and seminars. In addition, many emergency medicine experts join professional organizations like the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) to build their networks and learn about developments in their field.
A bachelor’s degree, medical school, residency, and board certification are all necessary steps on the long road to becoming an emergency medicine specialist. Emergency medicine experts who want to further their careers through fellowships or ongoing study can do so. If you’re thinking about a career in emergency medicine, you should know that you’ll need to get there.